Understanding Home Value as a Component of Net Worth
In today’s volatile real estate market, the relationship between your home’s value and your overall net worth has never been more critical. As a professional trader and investor, I’ve seen countless individuals fall into the trap of overextending themselves financially when purchasing a home. This is where Sam Dogen’s (Financial Samurai) revolutionary 30/30/3 rule comes into play, offering a powerful framework for making informed home-buying decisions.
Understanding the Home Buying Rule: The 30/30/3 Framework
Before diving deep into how this rule can transform your home-buying strategy, let’s break down its three core components:
“The 30/30/3 rule isn’t just another financial formula – it’s a protective shield against the most common pitfalls of home ownership in uncertain times.”
- The 30% Monthly Payment Rule: Your monthly mortgage payment should not exceed 30% of your gross monthly income
- The 30% Down Payment Rule: Have at least 30% of the home’s value in cash or semi-liquid assets
- The 3X Income Rule: The home’s value should not exceed three times your annual household gross income
Why Traditional Home Buying Rules Fall Short
Traditional wisdom often suggests putting down 20% and ensuring your monthly payments don’t exceed 28% of your gross income. However, this advice was formulated in a different era, with different economic realities. Today’s market requires a more conservative approach for several reasons:
- Increased Job Market Volatility
- More Frequent Economic Disruptions
- Higher Living Costs
- Greater Market Uncertainty
Data-Driven Home Buying Rule: Breaking Down the Numbers
Let’s examine how the rule translates into actual numbers for different home prices:
| Home Price | Required Down Payment (30%) | Maximum Monthly Payment | Required Annual Income |
|---|---|---|---|
| $500,000 | $150,000 | $2,500 | $166,667 |
| $1,000,000 | $300,000 | $5,000 | $333,333 |
| $1,500,000 | $450,000 | $7,500 | $500,000 |
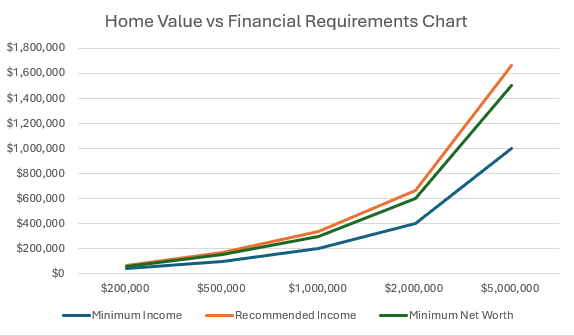
Visualizing the Relationship Between Home Value and Financial Requirements
Here’s a visualization of how home prices relate to required income and net worth levels:
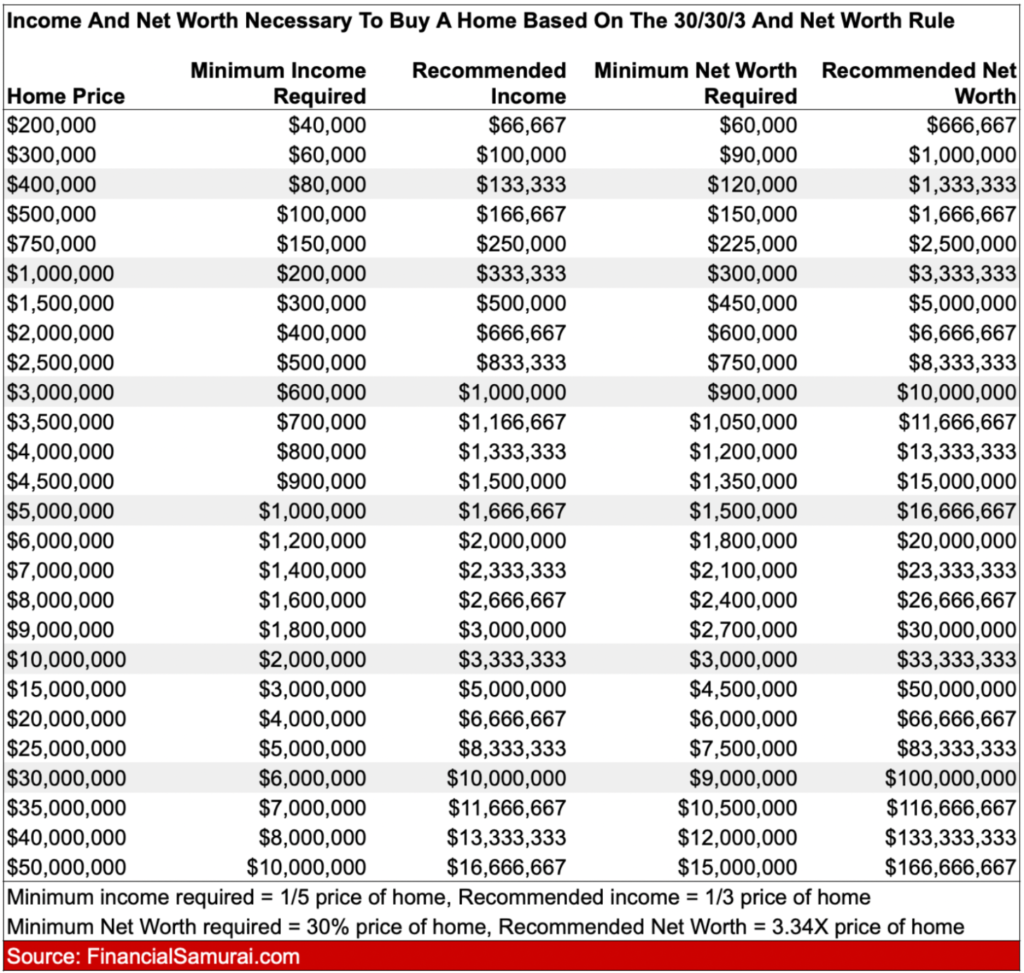
The Impact of Following the 30/30/3 Rule on Your Net Worth
Protection Against Market Downturns
Following the 30/30/3 rule provides significant protection against market volatility. With a larger down payment and manageable monthly payments, you’re better positioned to:
- Maintain payments during income disruptions
- Avoid forced sales during market downturns
- Build equity faster
- Maintain financial flexibility
Building Long-term Wealth
The conservative nature of the 30/30/3 rule actually accelerates wealth building through:
- Lower interest payments over the life of the loan
- Reduced risk of defaulting during economic downturns
- Greater ability to invest in other assets
- More financial flexibility for opportunities
Common Objections to the 30/30/3 Rule
“The Down Payment is Too High”
While 30% might seem excessive, consider the following benefits:
- Lower monthly payments
- Better interest rates
- Reduced private mortgage insurance costs
- Greater equity buffer against market downturns
“The Income Requirement is Too Restrictive”
The 3X income rule might appear conservative, but it:
- Ensures sustainable monthly payments
- Provides buffer for other life expenses
- Allows for continued saving and investing
- Reduces financial stress
Regional Considerations and Adaptations
High-Cost Markets
In expensive markets like San Francisco or New York, you might need to adapt the rule:
- Consider extending the income multiplier to 4X
- Look for properties with income potential
- Consider starting with a smaller property
- Explore up-and-coming neighborhoods
Low-Cost Markets
In more affordable markets, you might:
- Stick to the original 3X rule for maximum safety
- Use excess savings for property improvements
- Consider investment properties
- Build a larger emergency fund
Implementing the Smart Home Buying Rule: Your Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Calculate Your Numbers
Use these formulas to determine your home-buying budget:
- Maximum monthly payment = Monthly gross income × 0.3
- Maximum down payment = Available assets × 0.3
- Maximum home price = Annual income × 3
Step 2: Build Your Down Payment
Strategies for reaching the 30% down payment:
- Automated savings plans
- Investment in semi-liquid assets
- Side hustle income
- Gift funds from family (if available)
The Role of Net Worth in Home Ownership
Net Worth Allocation
Your home’s value as a percentage of net worth should typically:
- Not exceed 35% for those under 40
- Not exceed 25% for those 40-60
- Not exceed 20% for those over 60
Maintaining Balance
Strategies for maintaining a healthy net worth balance:
- Regular portfolio rebalancing
- Diverse investment strategy
- Regular net worth tracking
- Strategic debt management
Expert Resources and Tools
For more information on implementing the 30/30/3 rule, check out these valuable resources:
- [Financial Samurai’s Blog]: Detailed analyses and case studies
- [Real Estate Investment Calculators]: Tools for running your numbers
- [Personal Finance Forums]: Community discussions and experiences
- [Housing Market Analysis Tools]: Market research resources
Making the 30/30/3 Rule Work for You
Customization Strategies
Adapt the rule to your situation by:
- Adjusting for local market conditions
- Considering your career stability
- Evaluating your risk tolerance
- Assessing your long-term goals
Regular Review and Adjustment
Monitor your progress through:
- Quarterly net worth assessments
- Annual housing market analysis
- Regular budget reviews
- Emergency fund maintenance
Conclusion
The 30/30/3 rule represents a conservative but powerful approach to home buying that can help protect and build your net worth over time. While it may require more patience and discipline upfront, the long-term benefits of financial stability and wealth building make it worth considering for any serious home buyer.
“The most expensive home is not the one with the highest price tag, but the one that stretches your finances beyond their comfortable limits.”
Remember, your home should be both a place to live and a component of your overall financial strategy. By following the 30/30/3 rule, you’re more likely to achieve both objectives while maintaining financial flexibility for life’s other opportunities and challenges.
[Note: This blog post was written by a professional trader and investor based on personal experience and analysis of Sam Dogen’s 30/30/3 rule. All investment decisions should be made based on your personal financial situation and risk tolerance.]
Internal links for further reads: